IBAN is the internationally accepted ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) 13616-1:2007 compliant International Bank Account Number (IBAN) format for bank customer account numbers in the Kingdom of Bahrain. IBAN will: uniquely identify a bank customer account; and promote faster and more reliable electronic customer fund transfers.
ISO IBAN Standard for the Kingdom of Bahrain
The Central Bank of Bahrain issued the IBAN Standard for the Kingdom of Bahrain in February, 2011. The IBAN for the Kingdom of Bahrain consists of 22 alphanumeric characters:
Example of an IBAN: BH29 BMAG 1299 1234 56BH 00
| Country Code (2 Alpha characters) |
Check Digit (2 Numeric characters) |
Bank Identifier (4Alpha characters), First 4 letters of the bank’s SWIFT code “BIC” |
Core Bank Account Number (14 Numeric or Alphanumeric characters) |
| BH | 29 | BMAG | 1299123456BH00 |
The IBAN format for the Kingdom of Bahrain has been registered at SWIFT, which acts as the registration authority for IBAN formats. The IBAN registry is available at the SWIFT website.
IBAN Implementation
Retail banks started issuing IBANs to customers from 1st September, 2011. Banks and customers were required to use IBAN in making the following payments from 31st January, 2012:
- Domestic electronic payments to and from customer accounts of banks in the Kingdom of Bahrain;
- Cross-border outgoing electronic payments from customer accounts of banks in the Kingdom of Bahrain to customer accounts of banks/financial institutions in countries that have adopted IBAN (and made its usage mandatory); and
- Cross-border incoming electronic payments to customer accounts of banks in the Kingdom of Bahrain from customer accounts of banks/financial institutions in countries that have adopted IBAN as well as countries that have not adopted IBAN.
Banks will indicate the IBAN of the customer and SWIFT Code (BIC) of the bank in the header of the customer’s bank account statement(s).
Implementation of International Bank Account Number (IBAN) is an initiative of the Bahrain Economic Vision 2030 to improve the efficiency of electronic payments and further strengthen Bahrain’s status as the regional financial centre.
IBAN Standard Document
“ISO International Bank Account Number (IBAN) Standard for the Kingdom of Bahrain” document provides: the format of the IBAN for the Kingdom of Bahrain; scope, generation and usage of the IBAN; parties authorised to generate and issue IBAN; and the methodology for generation and validation of the IBAN.
FAQ
IBAN is the acronym for ISO 13616 Standard compliant International Bank Account Number.
IBAN is a unique customer account number which can be used confidently in making or receiving payments within the country as well as abroad. The confidence comes from two sources: the first is the internationally accepted standard for numbering bank customer accounts and the second is the ISO standard methodology for verifying the accuracy of the IBAN.
According to the ISO compliant IBAN Standard issued by the Central Bank of Bahrain (CBB) in February, 2011, all IBANs have a fixed length of 22 characters. Two examples of IBANs are given below:
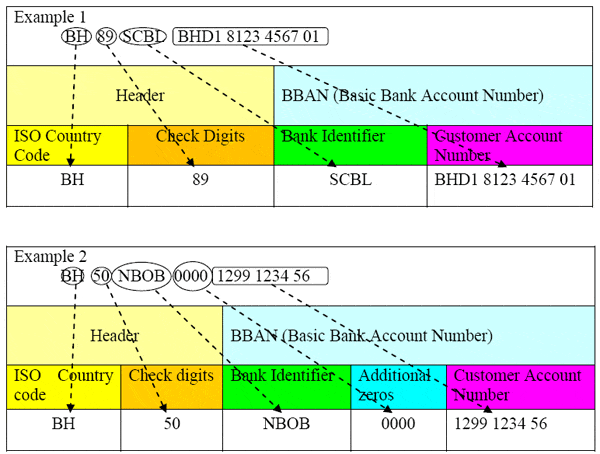
IBAN has two main components i.e. the header and the Basic Bank Account Number (BBAN).
The header helps to identify and verify the IBAN internationally. It contains the ISO two letter country code and the two check digits. Accordingly, the first 2 characters of an IBAN for Bahrain are always ‘BH’ (the ISO country code which identifies Bahrain, where the customer account resides). The third and the fourth characters of an IBAN are always the two check digits, generated by a bank in Bahrain, where the customer maintains his account.
The BBAN helps to identify an account number of a customer, as well as his bank, domestically. It comprises the Bank Identifier (which identifies the account holding bank) and the customer account number. In the case of Bahrain, the Bank Identifier is the first 4 letters of the SWIFT Code (BIC) of the respective account holding bank. The remaining part of the BBAN is the existing customer account number.
The length of the customer account number in the IBAN is fixed as 14 characters. It can contain numbers (0 to 9) and upper case letters (A to Z) depending on the respective bank. The length and structure of BBAN varies from country to country.
Example 1 (given above) is an IBAN of a customer account with 14 characters (alphanumeric).
In case of account numbers with less than 14 digits, the account number has to be padded with zeros to the left. Example 2 (given above) is an IBAN of a customer account number with 10 characters (numeric).
The Kingdom of Bahrain decided to implement IBAN to increase efficiency of electronic fund transfers.
The ISO IBAN Standard provides a methodology for a bank initiating a payment to check the accuracy of the IBAN of the recipient, regardless of the bank where he/she maintains his/her account. Therefore, any electronic payment containing a validated IBAN could be credited faster to the recipient’s account.
Having considered the benefits of IBAN in increasing the efficiency of local and cross-border electronic payments, Bahrain Economic Vision 2030 has included IBAN as a project for further strengthening Bahrain’s status as the regional financial centre.
The main benefit of IBAN to the customer is the assurance of making a payment to the correct account without delay.
Since banks check the accuracy of the IBAN at the point of initiating a payment, they can only make the payments which carry the correct IBAN.
Bank customers, who receive or make electronic payments in Bahrain or abroad, will require IBAN. If you have more than one account at your bank, you will require an IBAN for each of your accounts.
Bank customers can use IBAN for their interbank domestic and cross-border electronic payments from 31st January, 2012.
Each of your account numbers will be converted into IBAN format and will be informed to you by your bank, from 1st September, 2011. Your bank will also print your ΙΒΑΝ and bank SWIFT Code on your bank statement(s).
IBAN can be used for the following domestic and cross-border payments:
- Making an electronic payment (through a bank) to an account of a customer at a bank in the Kingdom of Bahrain;
- Receiving an electronic payment (through a bank) from an account of a customer in the Kingdom of Bahrain;
- Making an electronic payment (through a bank) to a person in a country that has adopted IBAN and the usage of IBAN is compulsory;
- Receiving an electronic payment (through a bank) from a person in a country that has adopted IBAN; and
- Receiving an electronic payment (through a bank) from a person in a country that has not adopted IBAN.
Yes, your bank will accept the payment and check the accuracy of the IBAN.
An IBAN can always be distinguished from a normal customer account number by the following:-
- Two letters at the beginning of the IBAN, which refer to the country code where the account resides;
- Two numbers (in the third and fourth position of the IBAN), which represent the check digit;
- Four letters (after the check digits) to identify the respective bank where the beneficiary maintains his/her account; and
- The length of the IBAN is 22 characters.
For example, an IBAN of a normal account number of BHD18123456701 is:
BH89 SCBL BHD1 8123 4567 01
It starts with “BH” (country code), followed by “89” (the two check digits), “SCBL” (bank identifier, which is the first 4 letters of the SWIFT Code (BIC) of the bank).
No existing customer account has this IBAN structure.
No. Your existing account number will continue to be valid. IBAN is not a new account number. It simply represents the existing account number in an electronically recognizable ISO standard format. The adoption of IBAN in Bahrain does not require changing or replacing the existing account numbers.
No. Customers have to use IBAN in making and receiving international as well as domestic electronic payments.
Only retail banks having customer accounts which are used for electronic payments are authorized to generate IBAN. No other party is permitted to generate IBAN for bank customers.
The procedure involved in using IBAN in an electronic fund transfer is explained below:
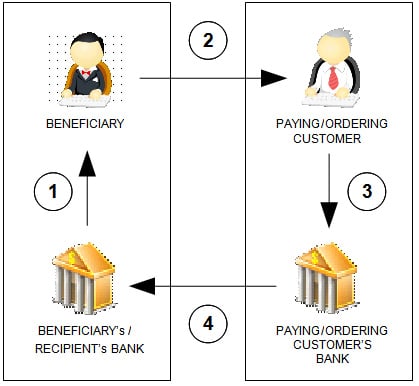
- The bank holding the beneficiary’s (recipient of the payment) account generates and provides the IBAN to the beneficiary;
- The beneficiary informs his/her IBAN to the paying/ordering customer;
- The paying/ordering customer submits an electronic fund transfer/payment order, which includes the beneficiary’s IBAN; and
- The paying/ordering customer’s bank validates/checks the IBAN in the outward payment message. After the receipt of the inward payment message, the beneficiary (recipient’s) bank validates the IBAN and credits the money to the beneficiary’s account.
Online tools to validate/check the structure of IBANs are provided by a number of organisations. One of them is the UN/CEFACT TBG5 IBAN ‘validator’ of UN/CEFACT United Nations Centre for Trade Facilitation and Electronic Business, which can be accessed via http://www.tbg5-finance.org/?ibancheck.shtml
When you write or print an IBAN on a document, it has to be split into groups of four characters, e.g.: BH50 NBOB 0000 1299 1234 56 to support easy recognition. The last group of the IBAN for a customer in Bahrain contains two characters.
There should not be any spaces when entering the IBAN in an electronic payment message. The IBAN should be presented in an electronic payment message as a continuous string of characters i.e. BH50NBOB00001299123456
76 countries (mainly member countries of the European Union) use IBAN (as at December 2018). In the Gulf region, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar and United Arab Emirates are using IBAN. Details of IBAN of those countries can be obtained from the IBAN Registry at the SWIFT website: https://www.swift.com/sites/default/files/documents/iban_registry_0.pdf
